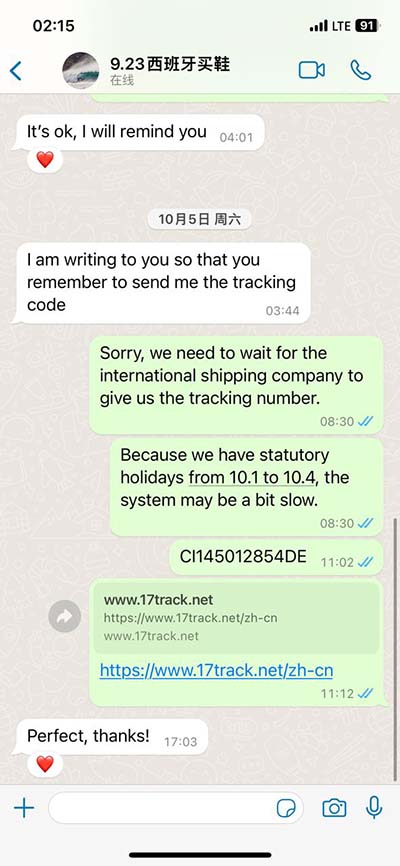
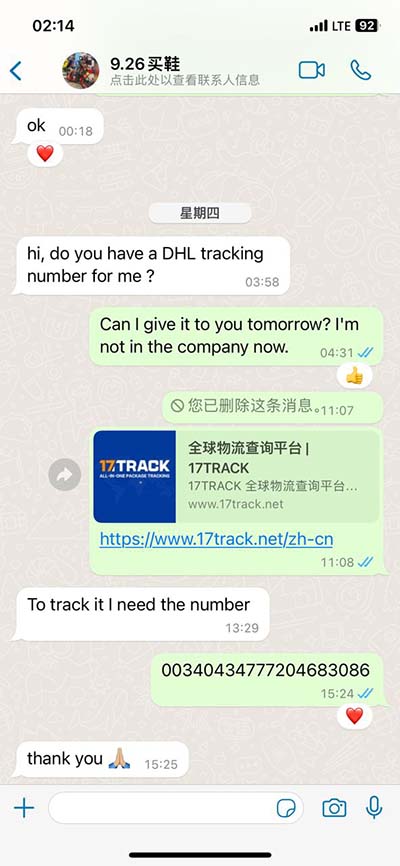
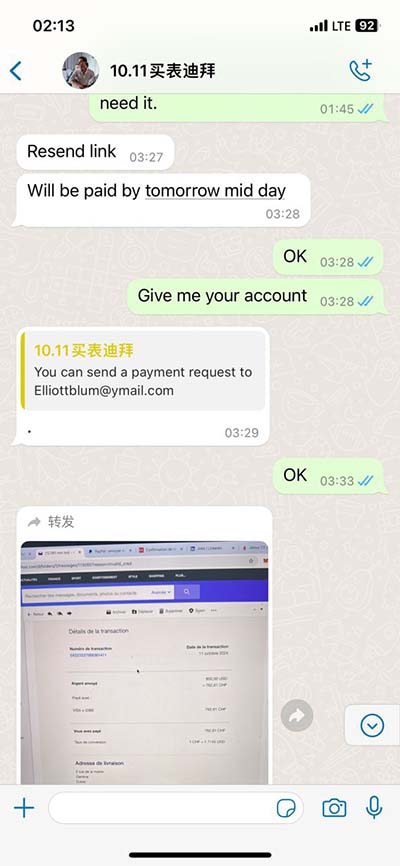
lv pressure trace | allows estimation of the left ventricular pressure trace area lv pressure trace A normalized LV pressure trace is individualized by adjusting for valve events and peak systolic blood pressure. The timing of valve events can be done either visually using the . Within the many choices, you can find models in a range of materials and sizes, from classic stainless steel or titanium, to 18K gold and platinum. Furthermore, all of the most famous watches from the past eight decades are there to discover, including the Seamaster 300, the Railmaster, Ploprof, Bullhead and Olympic Games tributes.
0 · allows estimation of the left ventricular pressure trace area
1 · Ventricular Pressure
2 · The assessment of left ventricular diastolic function: guidance and
3 · Should We Test for Diastolic Dysfunction? How and
4 · Pacing Optimized by Left Ventricular dP/dtmax
5 · Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction
6 · How to measure left ventricular myocardial work by
7 · Hemodynamics in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory of the
8 · Automatic detection of valve events by epicardial accelerometer
9 · Automatic detection of valve events by epicardial
Explore the Allure fragrance collection for Women at CHANEL. Shop the full collection on Chanel.com and discover your signature scent.
Measurement of the transmitral gradient by cardiac catheterization is frequently made with a simultaneous pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) and left ventricular (LV) . We estimated the LV pressure trace for an individual heart by scaling the isovolumic, ejection and filling phases of a normalized, averaged LV pressure trace to the time .The early diastolic flow into an incompliant LV causes LV pressure to rise rapidly and LA-LV pressures to equalise quickly with a consequently rapid deceleration of flow. The E wave .Overview of Factors That Contribute to Diastolic Function or Diastolic Dysfunction and Clinical Methods for Assessment. Diastolic function in combination with volume status (total body water) determines LV filling pressures, which when .
A normalized LV pressure trace is individualized by adjusting for valve events and peak systolic blood pressure. The timing of valve events can be done either visually using the .To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. . Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (due to SAM) leads to the extension of the systolic ejection phase and a decrease in ejection volume. It can also lead to coaptation of .We estimated the LV pressure trace for an individual heart by scaling the isovolumic, ejection and filling phases of a normalized, averaged LV pressure trace to the time‐points of opening and.
Left ventricular (LV) dP/dt max is measured invasively using a pressure-wire or pressure-volume catheter in the LV and provides a sensitive measure of the acute hemodynamic response to cardiac resynchronization .We estimated the LV pressure trace for an individual heart by scaling the isovolumic, ejection and filling phases of a normalized, averaged LV pressure trace to the time-points of opening and . Measurement of the transmitral gradient by cardiac catheterization is frequently made with a simultaneous pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) and left ventricular (LV) pressure. We estimated the LV pressure trace for an individual heart by scaling the isovolumic, ejection and filling phases of a normalized, averaged LV pressure trace to the time-points of opening and.
The early diastolic flow into an incompliant LV causes LV pressure to rise rapidly and LA-LV pressures to equalise quickly with a consequently rapid deceleration of flow. The E wave deceleration time is therefore short (< 150 ms) when diastolic impairment is advanced and .Overview of Factors That Contribute to Diastolic Function or Diastolic Dysfunction and Clinical Methods for Assessment. Diastolic function in combination with volume status (total body water) determines LV filling pressures, which when elevated, cause the cardinal symptoms of . A normalized LV pressure trace is individualized by adjusting for valve events and peak systolic blood pressure. The timing of valve events can be done either visually using the 2D image in apical three-chamber view, or by Doppler flow .
To generate a PV loop for the left ventricle, the left ventricular pressure (LVP) is plotted against the left ventricular volume (LV Vol) at multiple time points during a complete cardiac cycle. When this is done, a PV loop is generated (bottom panel of figure and linked YouTube video).
allows estimation of the left ventricular pressure trace area
Left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (due to SAM) leads to the extension of the systolic ejection phase and a decrease in ejection volume. It can also lead to coaptation of mitral leaflets and, as a result, to significant mitral insufficiency, which further impairs cardiac output.We estimated the LV pressure trace for an individual heart by scaling the isovolumic, ejection and filling phases of a normalized, averaged LV pressure trace to the time‐points of opening and. Left ventricular (LV) dP/dt max is measured invasively using a pressure-wire or pressure-volume catheter in the LV and provides a sensitive measure of the acute hemodynamic response to cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT).
Ventricular Pressure

The assessment of left ventricular diastolic function: guidance and
Should We Test for Diastolic Dysfunction? How and
search.alliance.mt
lv pressure trace|allows estimation of the left ventricular pressure trace area